kernel
Versions
https://kernelnewbies.org/LinuxVersions | https://kernelnewbies.org/Linux_5.15 (replace version#)
https://www.kernel.org/category/releases.html
Check
delete
Commit logs
https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/log/
.deb download
http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/ http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/daily/current/
Dynamic Kernel Module Support (DKMS)
https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Dynamic_Kernel_Module_Support
DKMS modules automatically rebuilt when a new kernel is installed.
Compiling
https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/community/blogs/5144904d-5d75-45ed-9d2b-cf1754ee936a/entry/kernel-build-system?lang=en (Chinese)
debug
.config
oldconfig: /boot/config* # compiled parameters Force pass overwriten: https://lists.kernelnewbies.org/pipermail/kernelnewbies/2013-May/008287.html
Install .deb manually
Ref: https://www.mf8.biz/linux-kernel-with-tcp-bbr/
initrd (initial ramdisk)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Initial_ramdisk initrd and initramfs refer to two different methods of achieving this.
initrd scheme
the image may be a file system image (optionally compressed) executes /sbin/init to begin the normal user-space boot process
initramfs scheme
available since the Linux kernel 2.6.13 the image may be a cpio archive (optionally compressed) Tiny Core Linux and Puppy Linux can run entirely from initrd.
dracut
create initial ramdisk images for preloading modules
/usr/lib/dracut/modules.d
mkinitcpio
https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Mkinitcpio mkinitcpio is the next generation of initramfs creation.
tracing
BPF /eBPF
https://qmonnet.github.io/whirl-offload/2016/09/01/dive-into-bpf/
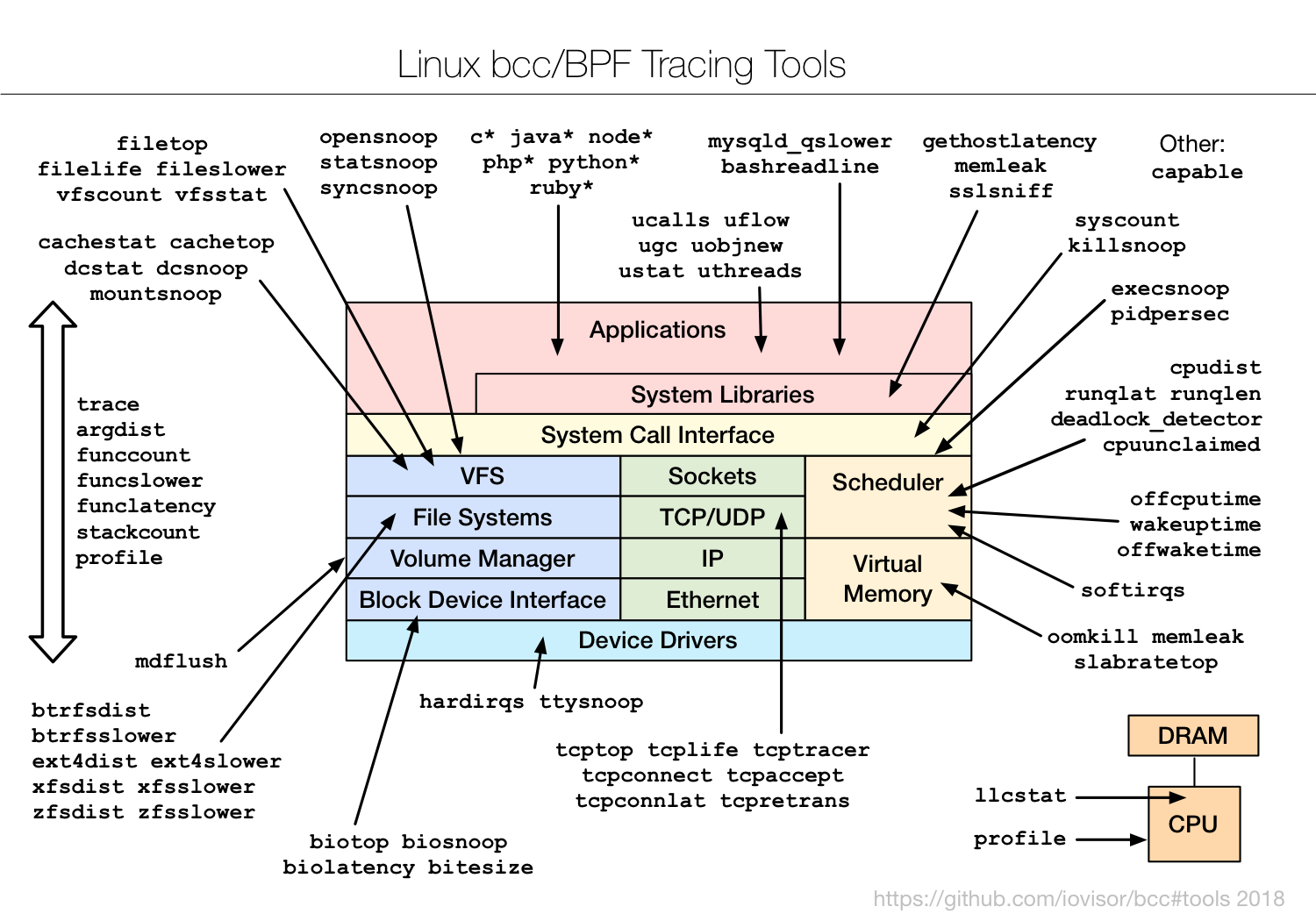
bcc
https://github.com/iovisor/bcc/tree/master/tools
Kernel Versions
+ for Longterm
linux-next
for patches aimed at the next kernel merge window https://www.kernel.org/doc/man-pages/linux-next.html
Last updated