Oracle
Storage
https://docs.oracle.com/cloud/latest/db112/CNCPT/logical.htm#CNCPT3000


A tablespace is a logical storage container for segments. Segments are database objects, such as tables and indexes, that consume storage space.
A segment is a set of extents allocated for a specific database object, such as a table. Each segment belongs to one and only one tablespace.
An extent is a set of logically contiguous data blocks allocated for storing a specific type of information.
One logical data block corresponds to a specific number of bytes of physical disk space, for example, 2 KB.
Tools
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/developer-tools/index.html
User
ALTER USER hr ACCOUNT UNLOCK;
ALTER USER hr IDENTIFIED BY hr_password;Create Table
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/server.111/b28310/tables003.htm#ADMIN11004 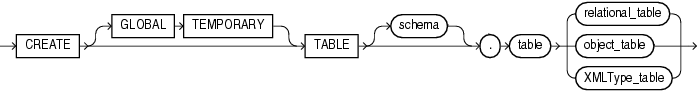
 https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/clauses002.htm
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/clauses002.htm
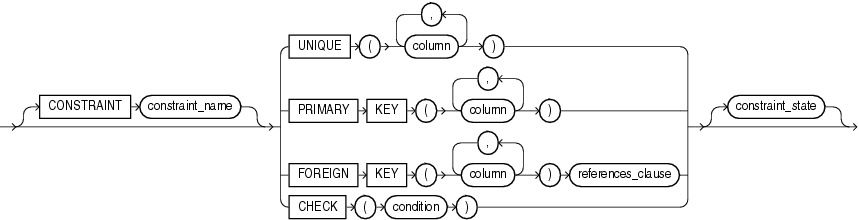

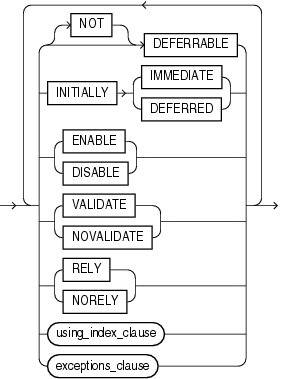
ORGANIZATION: the order in which the data rows of the table are stored.
HEAP: the data rows of table are stored in no particular order. This is the default.
INDEX: table is created as an index-organized table. In an index-organized table, the data rows are held in an index defined on the primary key for the table.
EXTERNAL: table is a read-only table located outside the database.
NOCOMPRESS -- whether to compress data segments to reduce disk use PCTFREE 10 -- NOCOMPRESS use the PCTFREE default value of 10, to maximize compress while still allowing for some future DML changes to the data INITRANS 2 -- Specify the initial number of concurrent transaction entries allocated within each data block allocated to the database object. MAXTRANS 255 -- deprecated. LOGGING -- a database object will be logged in the redo log file
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/server.111/b28286/clauses.htm#SQLRF021
 https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/server.111/b28286/clauses009.htm#SQLRF30013
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B28359_01/server.111/b28286/clauses009.htm#SQLRF30013
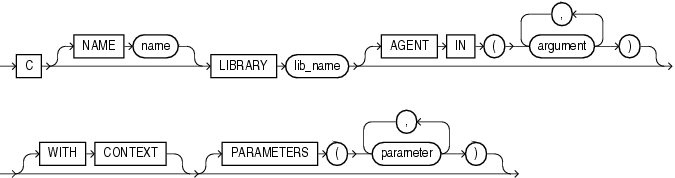
Create Procedure
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/statements_6009.htm 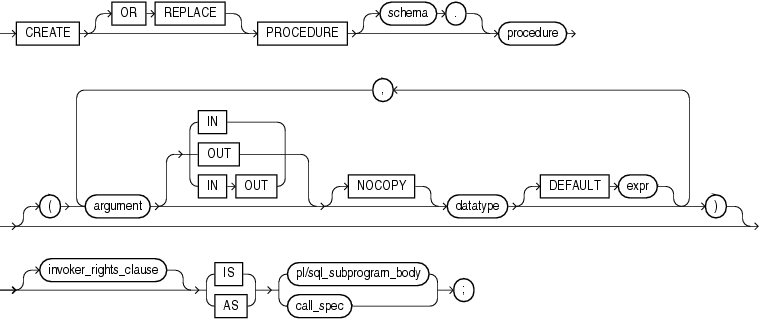
Use the call_spec to map a Java or C method name, parameter types, and return type to their SQL counterparts.

![]()
Last updated